Pythagoras was one of the greatest mathematicians ever to have lived, and it is to him we owe much of that which we now take for granted in geometry.
The most important of Pythagorasís theories, with respect to CCD drawing, is also his most famous. It is the rule that states:
"The square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides"
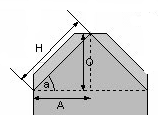
This refers to right-angled triangles. The hypotenuse of such a triangle is the sloped side, directly opposite the right (90į) angle. The "other two sides" are thus the two sides adjacent to the right angle, thus:

In this diagram, H is the hypotenuse, with A and O being the sides adjacent to the right angle of the triangle.
Within CCD, this rule is of use when calculating the required lengths of sloping wall panel edges, such as those used to marry with roof panels within building models. In mathematical terms, Pythagorasís rule is summarized by the equation:
H2=A2+O2
Thus, as long as at least two of the sides are known, we can calculate the third:
A2=O2-H2
O2=A2-H2
Related Topics: